Common ways through which hackers can enter
Now a days internet is so huge. No one can say that i am safe on internet, no one will attack my computer.
But every computer is a target for Hackers
Unprotected computers can be valuable for hackers because of their computing power and internet connections.A hacker can simply add it a botnet or use it as a zombie computer to send out spam and emails containing viruses and other malware, spread illicit materials.
Common ways through which hackers access a personal computer:
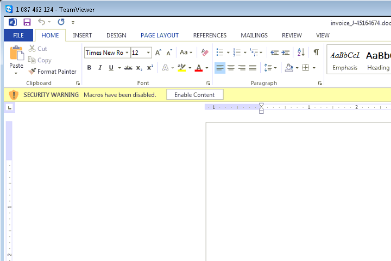
Emails containing viruses and malware :–
We are already posting lot of articles on that i.e. types of emails which spread malicious files, Malware etc. This is one of the most popular methods of spreading malware hidden in an attachment in the email. Once the attachment is opened, the malicious software executes and/or downloads onto the computer that receives it.
Hijacking ads :
Cybercriminals often place ads containing malicious code on legitimate websites. They do this either by purchasing ads directly, hijacking the ad server or hacking someone else’s ad account
Emails with links to malicious websites :
Spreading fake emails pretending to br from from well-known organisations that the receiver would tend to trust such as a bank or organisation . The html links lead to fake websites which try and trick the user entering sensitive information such as passwords and banking details. Sometimes these websites also attempt to install malware, viruses or spyware on the recipient’s computer.
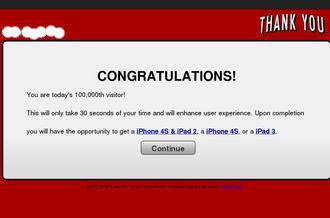
Malware sold as legitimate software :
Fake antivirus programs have infected millions of computers. Software is offered as free, available through the internet that includes malware designed to infect computers. Please don't use the unknown or free antivirus softwares.
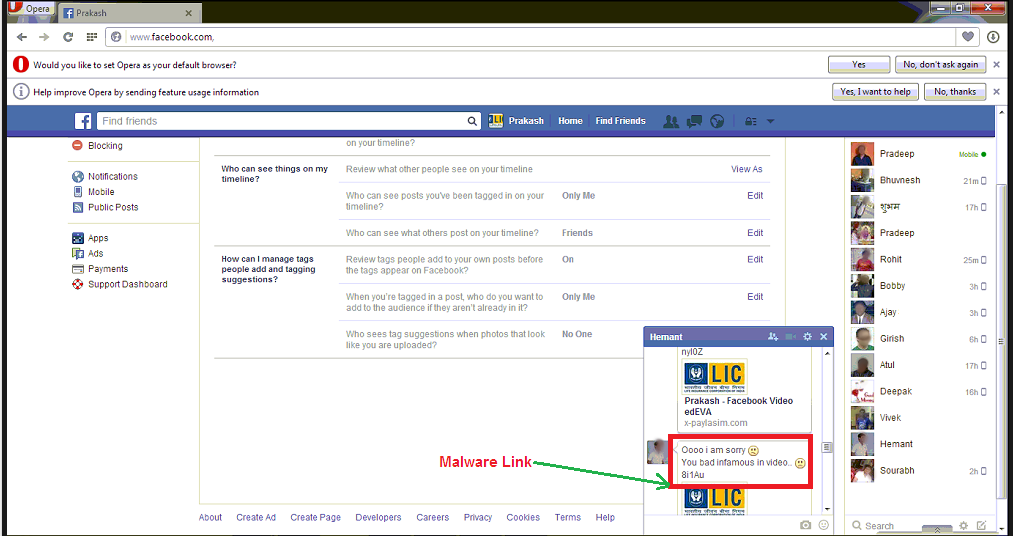
From Social networking pages :
By using social networking sites, a fake profile entices real users into following links to malicious websites or giving up sensitive personal information.
Probing for weaknesses :
Sometimes hackers send out mass emails in an attempt to compromise firewalls, intrusion detection systems and intrusion prevention systems to gain access to computer systems behind these defences. It’s a numbers game with millions of emails going out to identify malfunctioning, misconfigured or un-patched equipment
Inserting malicious packets:
This relies on access to a swathe of zombie computers to send out large quantities of data packets to a large number of recipients targeting a specific port. The aim is to identify a router or firewall with the specific port open and gain access to the computers behind the firewalls.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) :
APT means a sustained multi-pronged attempt to break into a specific organization’s or institution’s data networks. With APTs, hackers use many methods from sending fake promotional material to network attacks. The aim is to breach the network and steal information. APTs are different from other forms of attack because generally take place over the long term and can last months and years.