Malicious Payload Hidden in a Single Character: Google Calendar Becomes a New Cyber Weapon

Cybercriminals have devised an alarming new tactic by hiding malware in Google Calendar invites using invisible Unicode characters. This stealthy technique enables the delivery of malicious payloads through trusted platforms—bypassing traditional security mechanisms with a single deceptive character.
- Security researchers at Aikido discovered a malicious npm package named “os-info-checker-es6” using a vertical bar (“|”) embedded with invisible Unicode Private Use Area (PUA) characters to hide malware.
- These unprintable PUA characters encoded base64 instructions that ultimately connected to Google Calendar URLs for command and control (C2) operations.
- The technique allows attackers to deliver malicious payloads via Google Calendar invites, a platform widely trusted and used across personal and professional domains.
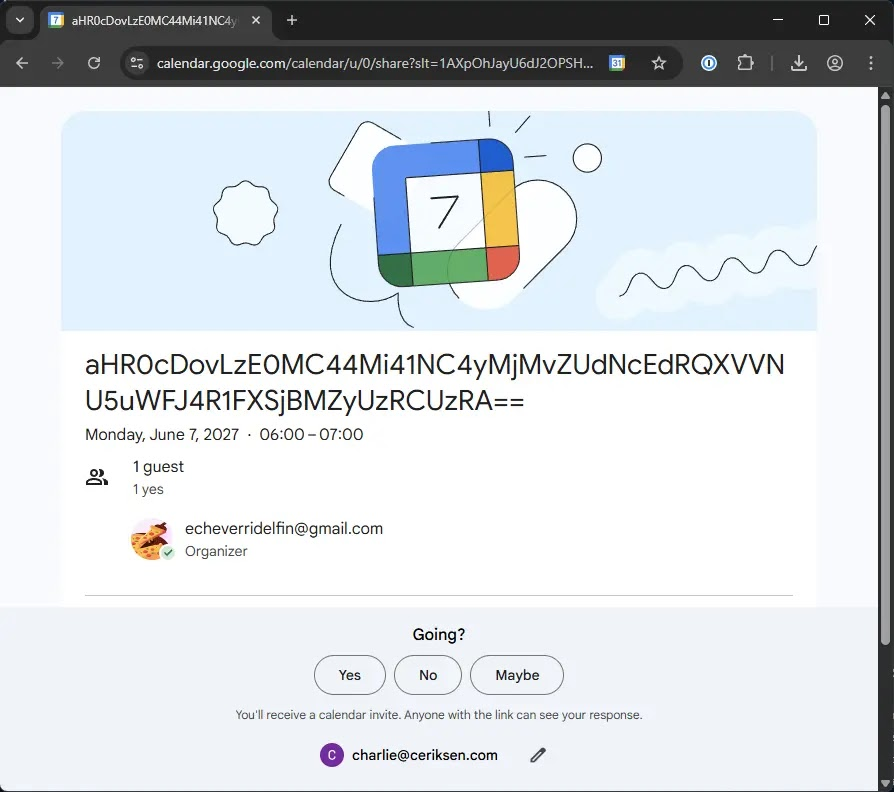
- Calendar invites contained encoded strings that led to attacker-controlled servers, enabling potential credential theft or financial fraud upon user interaction.
- Attackers used email header spoofing to make calendar invites appear legitimate, bypassing traditional email filters and phishing protections.
- Multiple npm packages were compromised, including:
- skip-tot
- vue-dev-serverr
- vue-dummyy
- vue-bit - All packages listed “os-info-checker-es6” as a dependency, expanding the attack surface.
- Google has acknowledged the threat and recommends users enable the “known senders” setting in Google Calendar to limit exposure.
- Additional safety tips include:
- Avoid accepting calendar invites from unknown sources.
- Inspect unexpected invites scheduled far in the future.
- Keep software dependencies and applications updated.
- Report suspicious calendar events using Google’s built-in reporting tools.
This attack reveals a sophisticated evolution in cybercriminal strategy—blending obfuscation with trust abuse. By hiding malware in what appears to be a harmless symbol and using a mainstream productivity tool as the vector, attackers have found a new way to slip past security defenses. Organizations and users must remain vigilant, review calendar settings, and monitor package dependencies to protect against these deceptive threats.
Comment(s)






