Hackers exploit ClickFix CAPTCHA scam to spread Ransomware
Cybercriminals have devised a new social engineering attack known as ClickFix, which abuses fake CAPTCHA verifications to trick users into installing malware, including ransomware and banking trojans like Qakbot. This attack exploits users’ trust in CAPTCHA systems, leading them to unknowingly execute malicious commands.
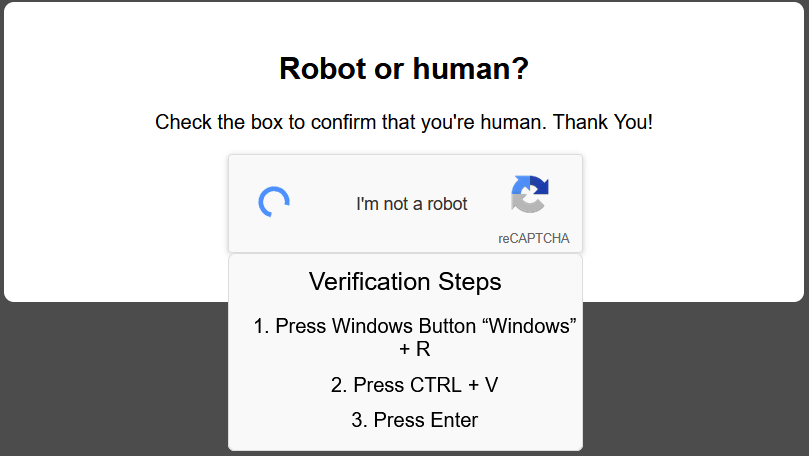
- Fake CAPTCHA Verification – Hackers use deceptive pop-ups mimicking legitimate bot verification processes.
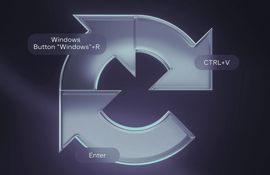
- Tricking Users with Keystrokes – Victims are instructed to press Windows Key + R, then CTRL + V, and finally Enter, unknowingly executing malware.
- Malware Deployment – Infostealers, ransomware, and banking trojans like Qakbot are delivered through Windows utilities like mshta.exe.
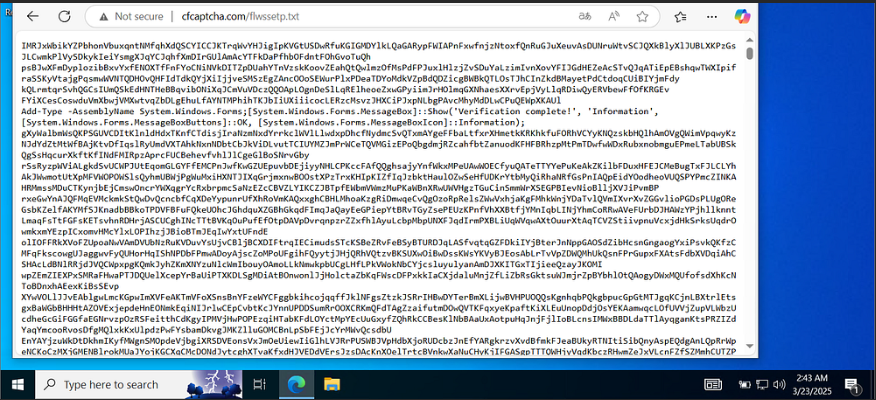
- Bypassing Security Measures – ClickFix leverages user interaction to evade traditional security detection.
- Obfuscation Techniques – Attackers use encryption, dynamic URLs, and PHP scripts to hide malicious activity.
Protect Yourself:
- Never trust unexpected CAPTCHA pop-ups – Legitimate websites don’t ask users to run commands.
- Avoid copying and pasting unknown text – Always verify the source before executing commands.
- Use strong security solutions – NPAV provides real-time protection against evolving cyber threats.
- Keep software updated – Regular updates help patch vulnerabilities and improve security.
ClickFix is a dangerous social engineering technique that weaponizes user trust in CAPTCHA systems to deliver ransomware and other malware. By understanding how this scam works and following best security practices, users can safeguard themselves from falling victim to such deceptive attacks. Stay alert, stay protected!
NPAV – Your Shield Against Cyber Threats!
Comment(s)






