Interlock Ransomware: New Threat Targets FreeBSD Servers with Double-Extortion Attacks

The newly emerged Interlock ransomware is designed to specifically target FreeBSD servers, exploiting the OS's prevalence in critical infrastructure environments. This ransomware operation, active since late September 2024, has already compromised several organizations, using a unique FreeBSD-based encryptor to execute double-extortion attacks, leaving critical services vulnerable.
- Targeted Platform: Interlock is among the few ransomware threats built to attack FreeBSD servers, alongside a Windows variant, which it also uses to compromise network devices.
- Double-Extortion Strategy: Interlock combines data encryption with data theft, leveraging stolen information to pressure victims into paying ransoms by threatening to publish sensitive files.
- First Known Attacks: Six organizations, including Wayne County, Michigan, have already fallen victim, with their stolen data publicly posted after refusal to pay the ransom.
- Unique Encryptor: The FreeBSD-specific ELF encryptor used by Interlock is rare, underscoring a deliberate attempt to target systems commonly found in critical infrastructure.
- Windows Version Features: Interlock’s Windows encryptor clears event logs and appends the .interlock extension to encrypted files, also dropping a ransom note, !README!.txt, in each affected directory.
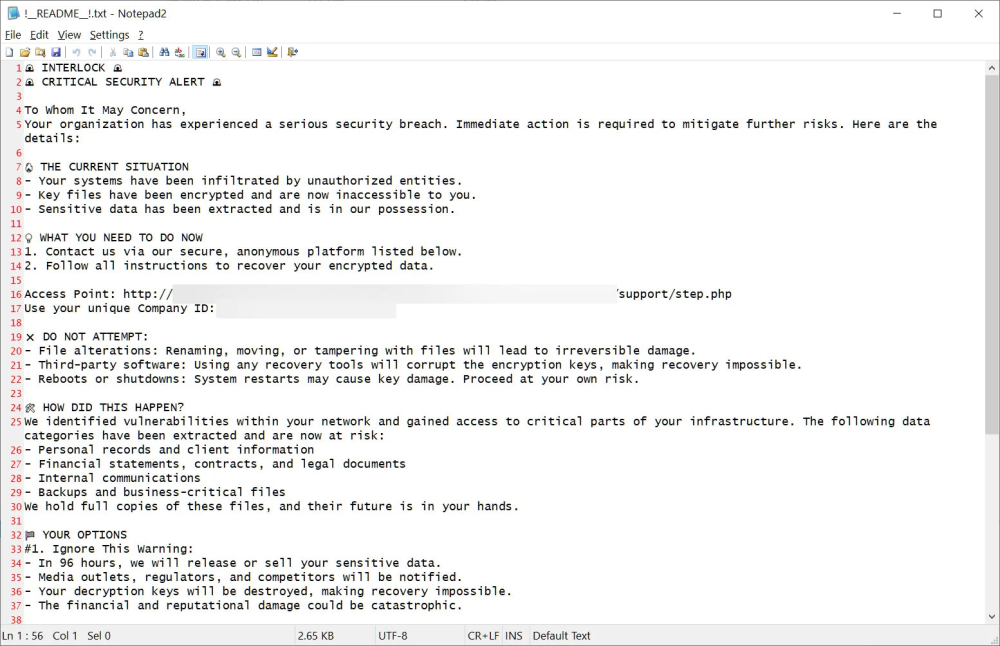
The Interlock ransomware represents a significant threat to FreeBSD-based servers, particularly those in critical infrastructure settings, where its impact can disrupt essential services. Organizations relying on FreeBSD systems are urged to review their security protocols and enhance defenses to mitigate this growing threat. With Net Protector Cyber Security solutions, businesses can safeguard their networks and ensure resilience against such sophisticated, targeted attacks.






