StalinLocker Deletes Your Files Unless You Enter the Right Code

A new in-development screenlocker/wiper called StalinLocker, or StalinScreamer, is discovered, which gives you 10 minutes to enter a code or it will try to delete the contents of the drives on the computer.
While running, it will display screen that shows Stalin while playing the USSR anthem and displaying a countdown until files are deleted.

When executed, StalinLocker will perform the following actions:
-
Extract the "USSR_Anthem.mp3" file to the %UserProfile%\AppData\Local folder and play it. This anthem is the same one heard in this YouTube video, but of much worse quality.
-
It will copy itself to %UserProfile%\AppData\Local\stalin.exe and create an autorun called "Stalin" that starts the screenlocker/wiper when the user logs into the computer.
-
It will create %UserProfile%\AppData\Local\fl.dat and write the current amount of seconds left divided by 3. So each time you start the program, the countdown is significantly less.
-
Attempt to terminate processes other than Skype or Discord.
-
Terminate Explorer.exe and taskmgr.exe.
-
Tries to create a Scheduled Task called "Driver Update" to launch Stalin.exe. This part of the code is currently throwing errors.
-
StalinLocker will then display the above lock screen that contains a 10 minutes countdown until your files are deleted or you enter a code. This code is derived by subtracting the current date of when the program was executed by the date 1922.12.30. If the user enters the correct code, the wiper will exit and delete the autorun.
On the other hand, if the code is not entered by the time the countdown reaches zero, the screenlocker will attempt to delete all of the files on each drive letter found on the computer. This is done by going through all drive letters from A to Z and deleting any that are accessible as shown below.
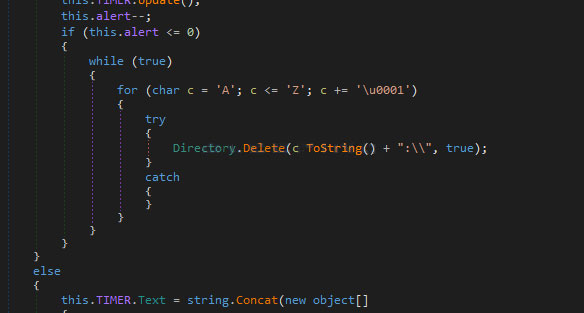
This wiper is currently in development, but could easily be made into a workable state. Thankfully, most security vendors are detecting this either through definitions or heuristics, so make sure that you have an npav anti-virus program installed and updated to the latest definitions.
Comment(s)






