Protecting Your Business: How to Recognize and Avoid Email Phishing Scams Using SmartExports
.png)
Phishing emails can appear to be legitimate messages from a trustworthy source, such as a bank, social media site, or online retailer. The goal of the email is to persuade the recipient to click on a link, download an attachment, or enter their login credentials on a fake website.
Phishing emails can be very convincing and may include logos, graphics, and text that look like they come from a legitimate source. However, there are often telltale signs that an email is a phishing attempt.
Phishing using a SmartExports link typically involves an attacker sending an email or message that appears to come from a trusted source, such as a bank or a legitimate company, and including a link to a fake SmartExports page. The page is designed to look like the real SmartExports login page but is actually a phishing site.
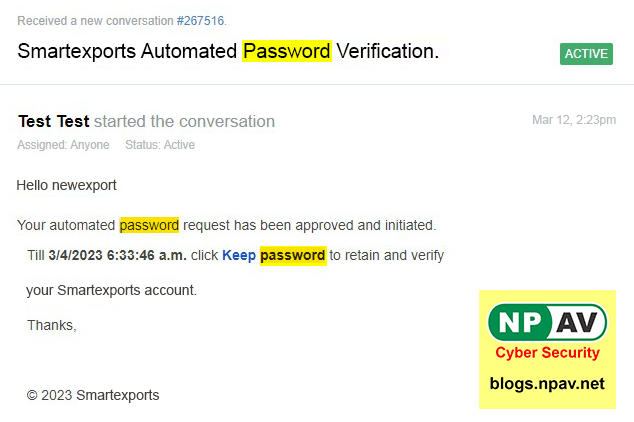
Look at this email, where an attacker tries to convince a user to retain his password by clicking on the link provided in this email, "Keep"
Once a user clicks on the link and enters their login credentials, the attacker can use this information to access the user's SmartExports account and steal sensitive data, such as customer information or financial records.
Here are some tips for identifying and avoiding phishing emails:
- To avoid falling victim to this type of phishing attack, it's important to always verify the authenticity of any emails or messages requesting your login information. You should never click on a link from an unsolicited email or message, and always manually enter the URL of the SmartExports website into your browser to ensure that you are visiting the genuine site. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication for your SmartExports account can provide an extra layer of security against phishing attacks.
Be wary of urgent or threatening messages: Phishing emails often try to create a sense of urgency or fear to get the recipient to act quickly without thinking. For example, an email might claim that your account has been compromised and you need to click on a link to reset your password immediately. Always take a moment to pause and evaluate the message before taking any action. - Don't click on links or download attachments: Phishing emails often include links or attachments that can infect your computer with malware or take you to a fake login page. Always hover over the link to see where it leads before clicking, and only download attachments from trusted sources.
- Check for grammatical errors or odd phrasing: Phishing emails are often written by non-native English speakers, so they may contain grammatical errors or odd phrasing. If the message seems too good to be true or doesn't quite make sense, it may be a phishing attempt.
- Use two-factor authentication: Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring a second form of identification, such as a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access to your accounts, even if they have your login credentials.
Phishing attacks can be very damaging, both to individuals and to organizations. By staying vigilant and following these tips, you can help protect yourself and your sensitive information from phishing scams.
Install NPAV on your systems to ensure best-in-class security against malware and ransomware attacks. Use NPAV and join us on a mission to secure the cyber world.






