Hackers Exploit ZIP File Concatenation Technique to Bypass Detection on Windows Machines

A new method in cyberattacks uses ZIP file concatenation to deliver malicious payloads undetected. By leveraging differences in ZIP parser handling, attackers can hide trojans in ZIP files, targeting unsuspecting users via phishing emails disguised as legitimate notices.
- ZIP Concatenation Technique: Hackers combine multiple ZIP files, each with separate content, into one archive to bypass detection mechanisms.
- Exploit of ZIP App Vulnerabilities: Different ZIP parsing tools, such as 7zip, WinRAR, and Windows File Explorer, interpret concatenated files differently, leading to varying visibility of hidden payloads.
- Phishing Email Delivery: Attackers lure users into downloading the malicious archive through phishing emails, often disguised as notifications for shipping or other services.
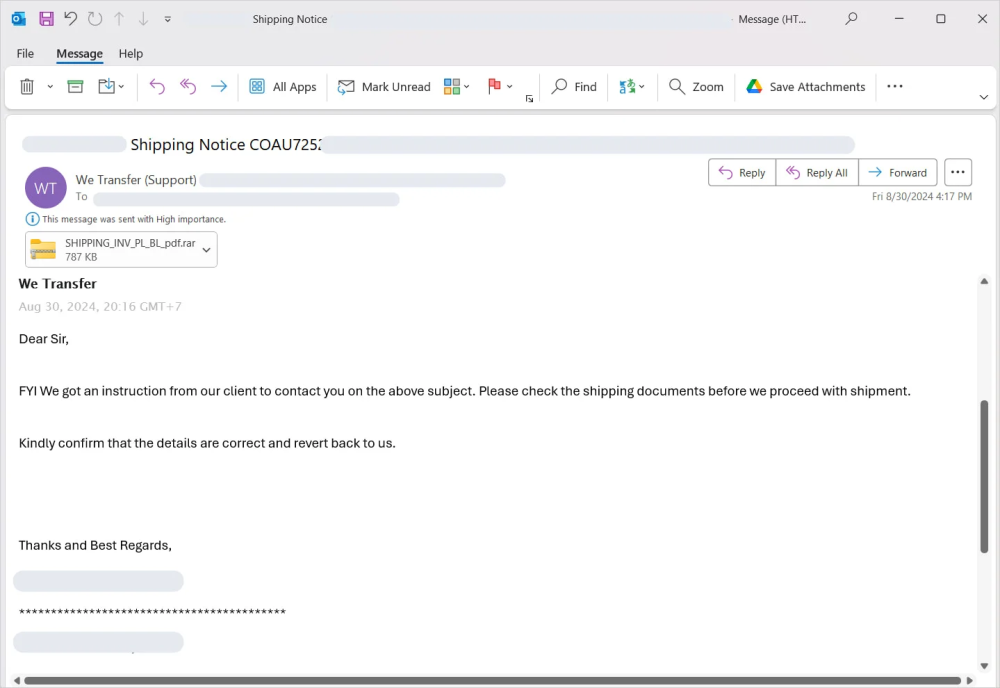
- Payload Concealment: Using AutoIt scripting, attackers automate malicious tasks without detection by traditional anti-virus software.
- Defensive Measures: Security experts recommend recursive unpacking in security solutions and strict email filtering policies for ZIP and RAR files.
The ZIP file concatenation technique underscores how attackers innovate to bypass traditional security measures. To counter such tactics, cybersecurity protocols must adapt by adopting advanced unpacking methods and stricter attachment handling policies to prevent trojan infections through malicious archives.
Comment(s)






