The Rising Threat of Rafel RAT: Cybercriminals Target Android Devices

In a concerning trend, multiple threat actors, including cyber espionage groups, are leveraging an open-source Android remote administration tool known as Rafel RAT to achieve their malicious objectives. This powerful toolkit has been camouflaged as popular apps like Instagram, WhatsApp, and various e-commerce and antivirus applications, making it a significant threat to unsuspecting users.
Powerful Capabilities for Malicious Actors
Rafel RAT, as analyzed by Check Point, provides cybercriminals with an extensive range of features for remote administration and control. Its capabilities include wiping SD cards, deleting call logs, siphoning notifications, and even acting as ransomware. These features enable attackers to conduct a variety of malicious activities, from data theft to device manipulation.
Notorious Deployments by Advanced Threat Actors
The Israeli cybersecurity company Check Point highlighted the use of Rafel RAT by the DoNot Team (also known as APT-C-35, Brainworm, and Origami Elephant) in previous cyber attacks. These attacks exploited a design flaw in Foxit PDF Reader to deceive users into downloading the malicious payloads. One such campaign carried out in April 2024, used military-themed PDF lures to distribute the malware.
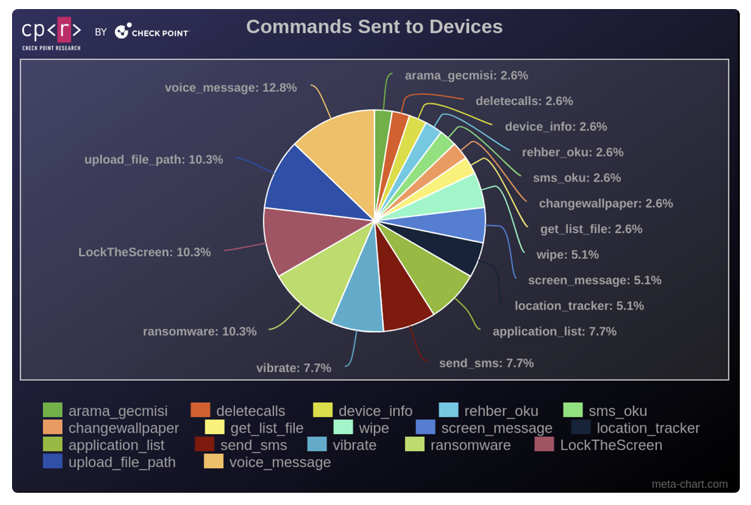
Widespread Campaigns and High-Profile Targets
Check Point's analysis identified around 120 distinct malicious campaigns utilizing Rafel RAT. These campaigns targeted high-profile entities across numerous countries, including Australia, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Russia, and the United States. The majority of the victims were users of Samsung devices, followed by those using Xiaomi, Vivo, and Huawei. Alarmingly, over 87.5% of the infected devices were running outdated Android versions that no longer receive security updates, making them particularly vulnerable.
Sophisticated Attack Chains and Social Engineering
The typical attack chains involve sophisticated social engineering tactics to manipulate victims into granting the malware-laden apps intrusive permissions. These permissions allow the malware to access sensitive data such as contact information, SMS messages (including two-factor authentication codes), location data, call logs, and lists of installed applications. Rafel RAT primarily uses HTTP(S) for command-and-control (C2) communications, but it can also employ Discord APIs to contact the threat actors. An accompanying PHP-based C2 panel enables registered users to issue commands to compromised devices.
A Case Study: Ransomware Operations
The effectiveness of Rafel RAT across various threat actors is further evidenced by its deployment in a ransomware operation likely originating from Iran. In this case, the attacker sent a ransom note written in Arabic via SMS, urging a victim in Pakistan to contact them on Telegram.
The Evolving Landscape of Android Malware
"Rafel RAT is a potent example of the evolving landscape of Android malware," Check Point noted. Its open-source nature, extensive feature set, and widespread utilization across various illicit activities underscore the growing sophistication of cyber threats. The prevalence of Rafel RAT highlights the critical need for continuous vigilance and proactive security measures to protect Android devices from malicious exploitation.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, it is imperative for users and organizations to stay informed and adopt robust security practices. The rise of tools like Rafel RAT serves as a stark reminder of the need for proactive defence mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information and maintain the integrity of our digital lives.






