Hackers Deploy Trojanized Minesweeper Clone to Target Financial Organizations

In a sophisticated cyberattack, hackers are leveraging a Python clone of the classic Minesweeper game to infiltrate European and U.S. financial institutions. The malicious campaign, attributed to the threat actor 'UAC-0188' by Ukraine's CSIRT-NBU and CERT-UA, disguises harmful scripts within the seemingly benign game code to install SuperOps RMM, a legitimate remote management software.
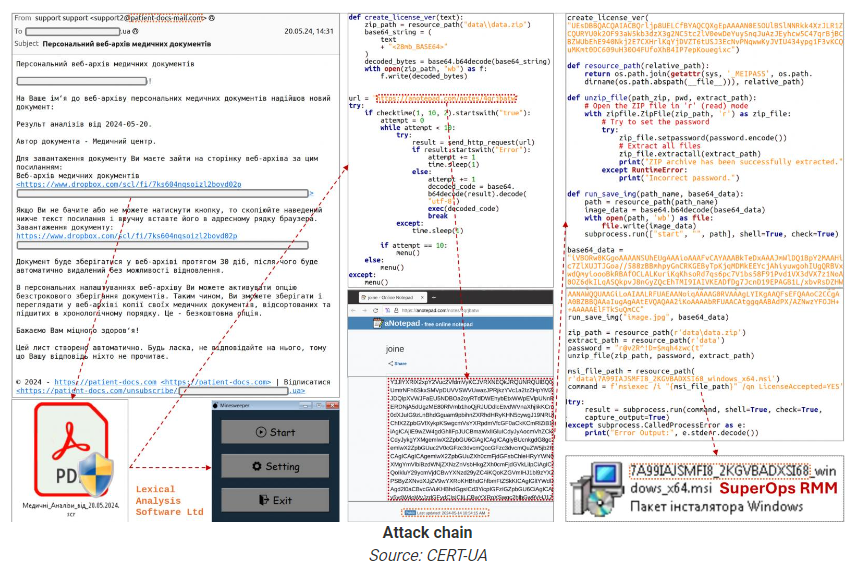
Attack Mechanics and Initial Discovery
The attack is initiated through phishing emails from "support@patient-docs-mail.com," masquerading as a medical center with the subject line "Personal Web Archive of Medical Documents." The email prompts recipients to download a 33MB.SCR file from a Dropbox link. This file, appearing harmless with its Minesweeper game code, conceals malicious Python scripts that further download harmful components from anotepad.com.
How the Attack Works
Camouflage: The Minesweeper clone’s code includes a function named "create_license_ver," repurposed to decode and execute the embedded malicious code.
Payload Delivery: The concealed code, a 28MB base64-encoded string, is decoded to produce a ZIP file containing an MSI installer for SuperOps RMM.
Execution: Using a static password, the MSI installer is extracted and executed, giving attackers remote access to the compromised systems.
Impact and Indicators of Compromise Research
following the initial discovery revealed at least five breaches in financial and insurance sectors across Europe and the U.S. CERT-UA advises organizations that do not use SuperOps RMM to regard any activity related to the software, or calls to its domains ("superops.com" or "superops.ai"), as indicative of a compromise. Additional indicators of compromise (IoCs) associated with this attack have been provided by CERT-UA for enhanced security measures.
This attack underscores the need for heightened vigilance and robust cybersecurity protocols, as threat actors continue to devise innovative methods to bypass defences and exploit legitimate software for malicious purposes.






