Blogs
-
Read moreDiscover how artificial intelligence is reshaping phishing tactics in cybercrime. Learn about AI-driven scams, deepfake technology, and the exploitation of messaging platforms.
-
Read moreA critical insecure deserialization vulnerability in N-able N-Central could allow attackers to execute arbitrary commands. Learn about the risks and recommended actions for organizations.
-
Read moreA critical vulnerability in GitHub Copilot (CVE-2025-53773) enables remote code execution through prompt injection attacks, compromising developers' machines. Learn how this flaw works and its implications.
-
Read moreA Haryana resident lost ₹10.2 lakh to a scammer impersonating a relative on Facebook. Learn how the fraud unfolded and the importance of verifying emergency requests.
-
Read moreA critical vulnerability in Fortinet FortiSIEM (CVE-2025-25256) allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands remotely. Learn about the risks and mitigation strategies.
-
Read moreMicrosoft has revealed a critical RCE vulnerability in Teams (CVE-2025-53783) that could let attackers read, write, and delete messages. Learn about the risks and fixes.
-
Posted: August 13, 2025Views: 47Read moreA report reveals that Delhi residents have lost INR 1,450 crore to cybercrime over the past decade. Learn about the rising scams and how to protect yourself.
-
Read moreLearn essential tips to secure your smart home IoT devices, routers, and smart speakers. Protect your home from cyber threats and ensure your privacy.
-
Read moreRoyal Enfield faces a significant ransomware attack, with hackers claiming full system compromise and demanding ransom. Learn about the implications and response.
-
Read moreResearchers unveil the 'Win-DoS Epidemic' at DEF CON 33, revealing new vulnerabilities in Windows that can turn servers and Domain Controllers into DDoS botnets. Learn more about the risks.
-
-
Read moreA serious flaw in a major automaker's dealer portal allows hackers to unlock and start vehicles remotely. Learn about the vulnerability and its implications.
-
Posted: August 11, 2025Views: 75Read moreA DRDO employee in Hyderabad has fallen victim to a fake investment scam on WhatsApp, losing ₹54 lakh. Learn how the scam operated and the warning signs.
-
Read moreGoogle's Salesforce instance was compromised by the ShinyHunters group using voice phishing tactics. Learn about the breach and the exposed records.
-
Read moreHackers exploit a legitimate driver to bypass Microsoft Defender and install Akira ransomware. Learn how this vulnerability works and how to protect your PC.
-
Read moreSocket’s Threat Research Team has uncovered over 60 malicious RubyGems packages that steal social media and marketing credentials. Learn how these infostealer tools operate.
-
Read moreThe GreedyBear cybercriminal operation has stolen over $1 million in a massive cryptocurrency theft campaign using 650+ malicious tools. Learn how they exploit browser extensions and AI.
-
Read moreCybercriminals compromised corporate systems in under five minutes by exploiting QuickAssist and PowerShell scripting. Learn how social engineering facilitated this rapid breach.
-
Read moreA Florida woman was tricked out of ₹12.5 lakh ($15,000) by scammers who cloned her daughter's voice in a deepfake emergency scam. Learn about this rising threat of AI-powered voice fraud.
-
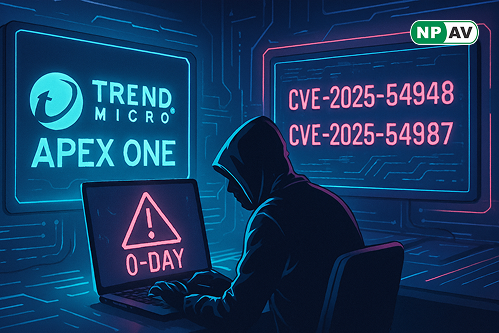
Read moreTwo critical zero-day vulnerabilities in Trend Micro Apex One (on-prem) devices, CVE-2025-54948 and CVE-2025-54987, are being exploited in the wild. Learn about their impact and mitigation strategies.